Articles and Books
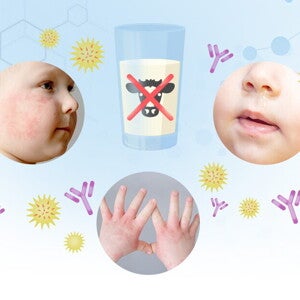
Unraveling Cow's Milk Protein Allergy (CMPA) in Infants and Young Children
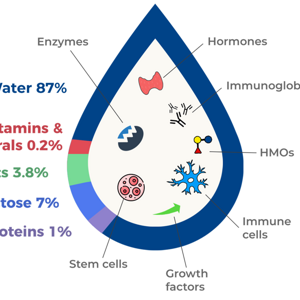
From Lactation to Health: The Benefits of Human Milk Bioactives
Disorder of Gut-Brain Interaction: Insights, Causes and Management
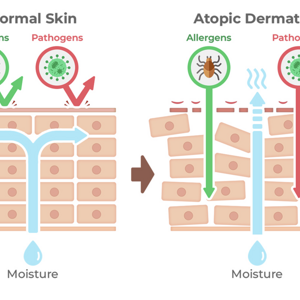
Addressing Atopic Eczema Early in Life to Reduce the Risk of Atopic March
Pivoting the Science of Biotics for Clinical Applications

Reducing the Risk of Preterm Birth Through Maternal Nutrition Interventions
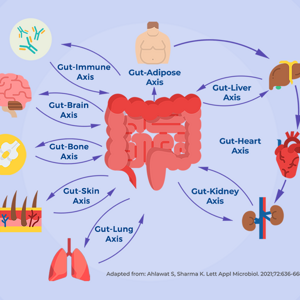
How the Gut Microbiome Shapes Health: The Role of Gut-Organ Connections

The True Weight of the Obesity Epidemic: Factors and Implications

Midwife News Healthy For the Future! Vol. 3 - 2023

Iron-Fortified Foods Are Needed To Meet the Estimated Average Requirement for Iron in Australian Infants Aged 6 to 12 Months

HMOs and the Shaping of Microbiome Maturation: Review of Evidence and Clinical Implications


