Breastfeeding Center
Let's Protect, Promote and Support Breastfeeding
Human milk provides unparalleled nutrition to infants in the early stages of life. WHO/UNICEF recommend exclusive breast-feeding for the first 6 months of life, with the introduction of complementary food at the age of 6 months, and continuation of breastfeeding for as long as mutually agreeable by the mother and the infant
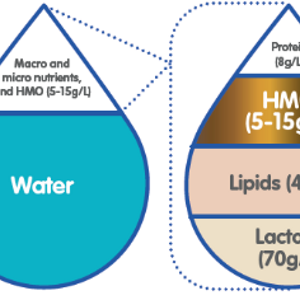
Breast milk is a comprehensive source of energy and macronutrients, as well as bioactive micronutrients essential for the growth and development of an infant.
Infants fed human milk have different gut microflora, exhibit different growth patterns, and even face a lower long-term risk of chronic diseases, such as obesity, types 1 and 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Publications

Annales Nestlé Article: Breastfeeding during a Pandemic

Lactation for Infant Feeding Expertise (LIFE) Abstract book

Breastfeeding & Cow Milk Protein Allergy: What You Need to Know

NNIW94 - Milk, Mucosal Immunity & the Microbiome: Impact on the Neonate
Videos

NNIW97: Past, Present, and Future of Human Milk Research - Sagar Thakkar
NNIW96: Donor Milk Banking- Safety, Efficacy, New Methodologies

Interview with Valerie Verhasselt : Influence of Breastfeeding on Immune Trajectory

NNIW96: Human Milk Bioactives – Future Perspectives
Infographics

Keeping a healthy outlook for mothers and babies during breastfeeding

Human Milk Oligosaccharides: A Child Health Guardians

Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Help Strengthen Immunity in infants