Gut Microbiota
Microbiota is the good (and bad bacteria) in your gut. Every human being carries about 1-2kg of gut microbiota representing a number of cells far bigger than all our body cells together. Here we provide the latest science on the relation between nutrition, gut microbiome, immune system and human health.


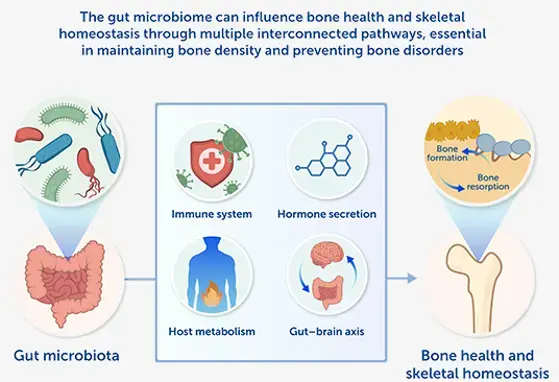
Educational Symposium supported by NNI on Microbiota and Bone, presented at European Calcified Tissue Society Congress (ECTS)

Microbial Products Derived From Human Milk Oligosaccharides Fermentation by Infant Microbiota Protect Against Inflammation-Mediated Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction In-Vitro

Human Milk Oligosaccharides Confer Resistance against Inflammation-mediated Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction In-Vitro

Video Teaser: Gut Discomfort in Toddlers: Can Nutrition Bring a Solution?

Human Milk Oligosaccharides: A Child Health Guardians

Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Help Strengthen Immunity in infants