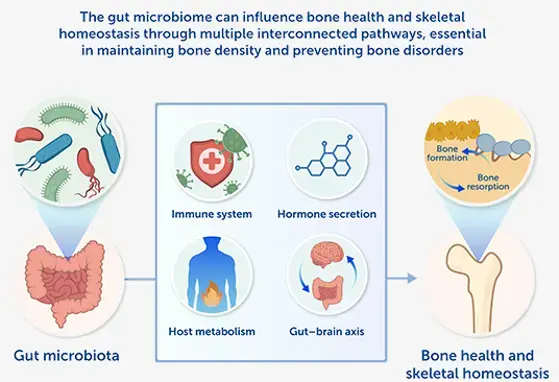
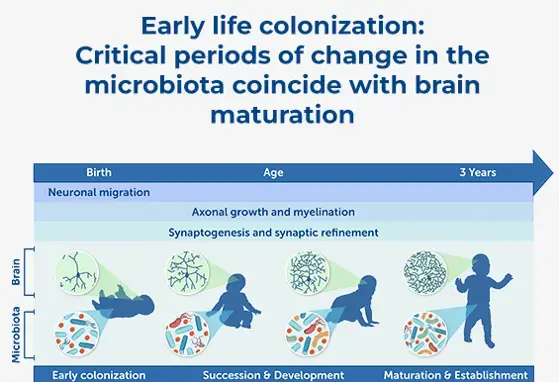
Gut Microbiota
Microbiota is the good (and bad bacteria) in your gut. Every human being carries about 1-2kg of gut microbiota representing a number of cells far bigger than all our body cells together. Here we provide the latest science on the relation between nutrition, gut microbiome, immune system and human health.

Researchers create map of the gut's microbial landscape

European Academy of Pediatric Societies (EAPS) 2018

Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Factors Affecting their Composition and their Physiological Significance

Physiological Effects of Feeding Infants and Young Children a Formula Supplemented with Milk Fat Globule Membranes


Breast Feeding in Medicine a Historical Perspective

Human Milk: Composition, Clinical Benefits and Future Opportunities

Human Milk MicroRNAs/Exosomes: Composition and Biological Effects