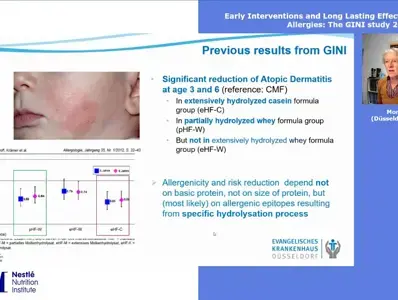
Allergy development is a complex process and depends on numerous factors, including postnatal influences, that guide the immune system towards allergenicity or tolerance. Breast-feeding has a proven beneficial role and some studies also support a preventative effect of partially hydrolyzed infant formula on allergy development. Professor Monika Gappa presented the 20-year follow-up data from the GINI study showing that early nutritional intervention with extensively hydrolyzed casein formula (eHF-C) or partially hydrolyzed whey formula (pHF-W) when compared to cow’s milk based formula exerts a preventive effect on both eczema and allergic airway manifestation that endures until adulthood.